
Security advisory is not just about updating, it’s more comprehensive, and more important.
We often hear or see ‘Security Advisory’ on news channels and social media platforms, mentioning how many products and companies are affected, large corporations and many institutions are working on patches, or how hackers are causing digital asset and financial losses.
What is security advisory anyways? What should I do if I don’t quite understand it?
Simply put, a security advisory is an industry-standard method used by governments, businesses, and organizations to collect and compile cybersecurity intelligence. A security advisory is issued when there is a need to inform all internet users and relevant users about potential security threats, vulnerabilities in products, software, services, and the corresponding remediation and repair measures.
What specific contents are included in a security advisory? It usually includes a detailed description of the security vulnerability, the affected products and versions, solutions or mitigation measures, and information about the updates. The purpose of a security advisory is to ensure that all affected users are promptly informed about the severity and scope of the issue, and take action as soon as possible to prevent the security vulnerability from being maliciously exploited. This way, users can protect the data in their devices and services, as well as the overall system security, to avoid further harm.
However, if each vendor has their own vulnerable data, with different formats, how can we know if your vulnerability is not the same as mine? When discussing security risks and vulnerabilities, how can we ensure that everyone is talking about the same thing?
There is a globally recognized system for security vulnerability identification, known as the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database, which specifically collects and assigns numbers to various security weaknesses and vulnerabilities worldwide to make it easier for users around the world to query and view.
In this way, all cybersecurity equipment, hardware and software vendors, antivirus software, endpoint software and the like can have a unified cybersecurity vulnerability identification number. This serves as the basis for automated communication and production of security content.
All CVEs are assigned a unique identification number for each vulnerability, and the format is as follows:
CVE-YYYY-NNNN
CVE is a fixed prefix, YYYY is the year in the Gregorian calendar, and NNNN is a serial number indicating the chronological order. NNNN is typically a four-digit number. If it is less than four digits, leading zeros are added. When necessary, it can be extended to five digits or more. In recent years, due to rampant hacker activities, the number of security researchers has also increased and more security vulnerabilities have be discovered. As a result, CVE codes have generally been extended to five digits.
What is Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)?
With CVE to identify all known security vulnerabilities, the next step is to assess their risk. This is where the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) comes in, which provides the public with a score indicating the severity of each CVE vulnerability.
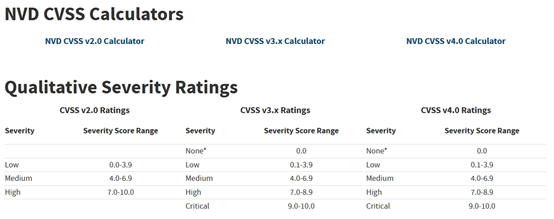
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) maintains the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which lists the scores and severity ranking calculated using different versions of the CVSS.
CVSS was initiated by the National Infrastructure Advisory Council (NIAC) in the United States. The basic score is generated by considering technical details and relevant attributes of vulnerabilities, such as attack complexity, confidentiality, integrity, and availability, as well as time and environmental factors. Therefore, the overall score presented is highly professional and serves as a standard assessment tool in the cybersecurity field. This allows us to have a consistent evaluation method to judge the impact of different software and cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and aids in the decision-making process for appropriate response measures.
The higher the score of a CVE vulnerability, the more urgent it is to prioritize and promptly patch it. This is also the effort made by many cybersecurity professionals, researchers, and software and hardware developers in their respective fields.
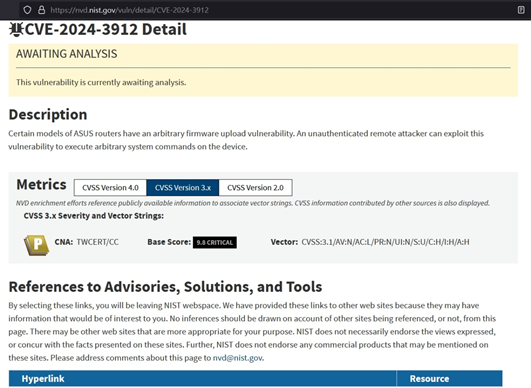
Security advisory related to ASUS router contains a CVSS score. Typically, scores above 7 are considered high and require priority patching. Scores above 9 are extremely severe and need immediate patching to ensure security.
Are there different levels of vulnerabilities?
The industry has also established severity levels for the aforementioned CVE and CVSS. These levels are assigned based on the CVSS score of the vulnerability. The levels range from V5 (Critical) to V1 (Information), with the highest level requiring priority handling.
Finally, there is the status, which defines the status of each security vulnerability. The status is continuously updated in these security databases based on the time and actions taken by vendors. The statuses include: Investigating, Not Affected, Fixing, Resolved, and Information, among others. This makes it easier for us to identify whether the risk of these vulnerabilities still exists and to take appropriate measures.
Based on the key information above, we can see that a standard security advisory typically includes the following elements:
- Vulnerability description: Detailed explanation of the nature and scope of the vulnerability.
- Affected products and versions: List all affected software or hardware versions.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate the potential threat level posed by the vulnerability.
- Solution and mitigation measures: Provide recommendations for fixing the vulnerability through updates or configuration changes.
- Update file information: If there are patches or updates available, provide download links and installation guides.
Security advisory of major international vendors
Internationally renowned vendors such as Microsoft, Apple, and Google attach great importance to cybersecurity reporting. They usually have dedicated security teams responsible for monitoring and issuing advisories. For example, Microsoft’s monthly “Patch Tuesday” is a regular security update cycle that provides detailed security information and patch updates. These security advisories are not just defensive measures but also part of the companies’ commitment to user security, aimed at enhancing overall network security.
For example, Google’s Android platform is used in a massive number of Android mobile devices, industrial devices, and entertainment equipment worldwide. New security version information is regularly released on Google’s website. This includes the version numbers that different versions of the Android system will be updated to in the recent updates, a summary of the bugs fixed, security vulnerabilities addressed, and new features. However, the detailed contents of the fixes are not publicly disclosed, as such information can only be accessed from Google’s developer community. Google also releases information to relevant Android vendors, including detailed information about version updates and a list of changed files for the vendors to upgrade their versions.
As the primary maintainer of a major global platform, Google will notify all listed issues in advance to their global Android partners. The source code patches for these issues are also released to the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) repository along with different versions of Android to allow developers from partners to access, develop, test, and implement the patches.
A well-known major company in the cybersecurity industry, Fortinet, is a supplier of firewall devices, switches, and security equipment for many enterprises, institutions, and industrial OT sectors, so in a similar manner, the company’s security advisories will explain encountered security issues. For example, a common SSL-VPN security vulnerability would prompt Fortinet to recommend that users of their equipment update to the latest firmware and enable the updating feature, so that the equipment and users can more securely connect to the company network via VPN.
Each device firmware update will include a long list of system program fixes, improvements to existing issues, and notifications of potential future problems.
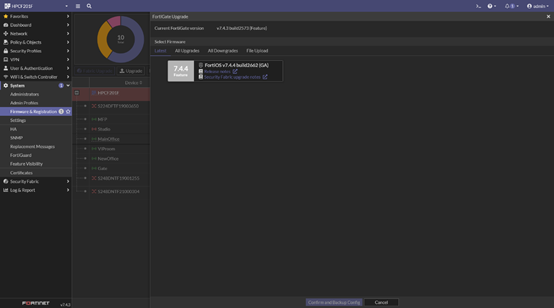
A Fortigate device will need to back up the relevant configuration files and perform an update when an alert appears. However, before performing these actions, the official security update advisory should be consulted to understand which services or functions will be affected and what items are included in the update.
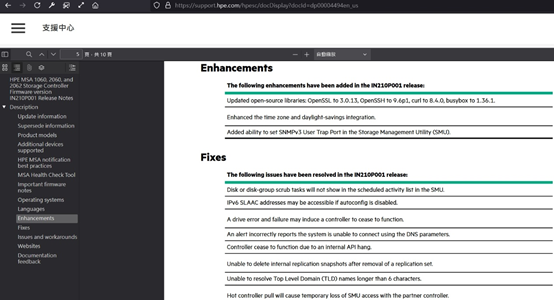
HPE, a major storage device manufacturer, will release update announcements for its devices, and list the version names of different devices as well as the content that will be updated and enhanced. For example, when the versions of open-source packages are upgraded, such as OpenSSL to 3.0.13, OpenSSH to 9.6p1, curl to 8.4.0, and busybox to 1.36.1, the updates will specify the new software version numbers.
Other fixes and details are listed below. For more detailed information, customers would need to request it directly from HPE. Public announcements on the internet are typically in a relatively simplified form.
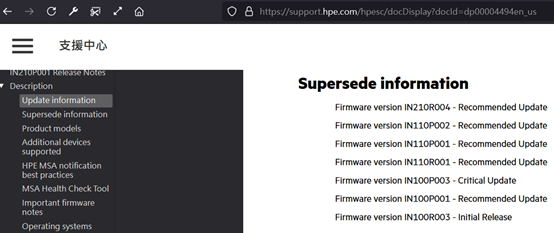
Common open-source software in the market also responds to encountered CVEs with software update notifications, detailing the improvements made in each update.
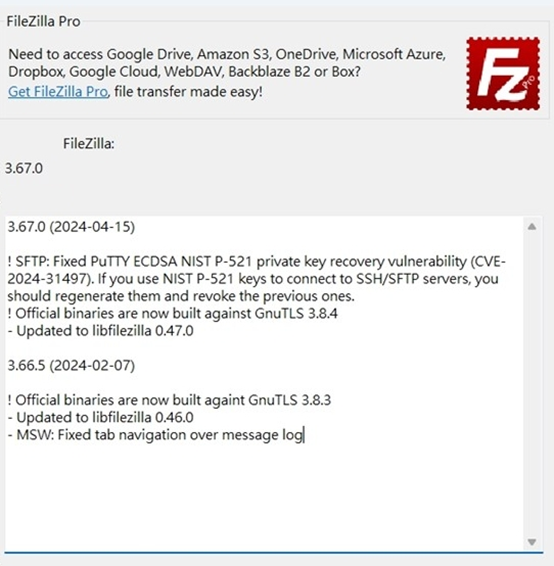
An example is FileZilla, a well-known FTP software. The latest version has fixed a security vulnerability (such as CVE-2024-31497) related to private security keys. The vulnerability has also been patched in this update.
What is QNAP security advisory?
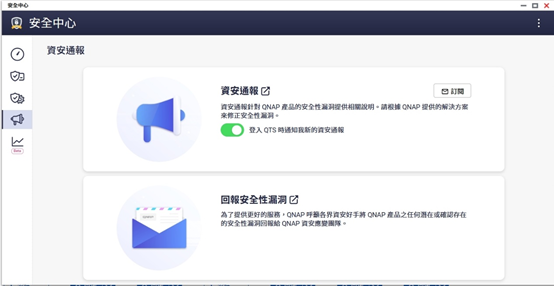
QNAP has many years of global service and market experience, and places significant emphasis on cybersecurity issues for its customers. QNAP’s security advisory mechanism includes the following aspects:
Regular annual firmware updates: QNAP consistently releases firmware updates for its devices, along with security patches and updates for associated operating systems to address known vulnerabilities.
Security advisories: On the QNAP official website and the default homepage when users log into the QTS system, there are automatic reminders of security advisories. Details about potential security threats and remediation measures are provided by clicking on the update dates. By reading such information, users can understand the approximate scope of impact and the content of the system updates.
Professional team: QNAP has dedicated cybersecurity team, such as QNAP PSIRT, which is responsible for monitoring the latest security threats and responding as quickly as possible.
What can QNAP users do?
As a QNAP NAS user, you can take the following measures to protect your device and data security:
Regularly check for updates : Check and install software updates and patches released by QNAP regularly.
Enable security settings: Set strong passwords, enable two-step verification, restrict external access, and other security measures.
Monitor the system: Use the monitoring tools provided by QNAP to stay informed about the device’s operational status and potential threats.
Back up data: Back up important data regularly to ensure quick recovery in the event of an attack or failure.
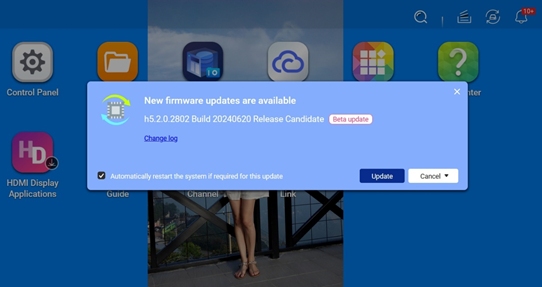
When there is a firmware update, you can click to view the version information. The updated content will be displayed for users to stay informed.

You can click on the firmware update changelog to see a summary of important content for the update, including fixes for security vulnerabilities and enhancements to system functionality.
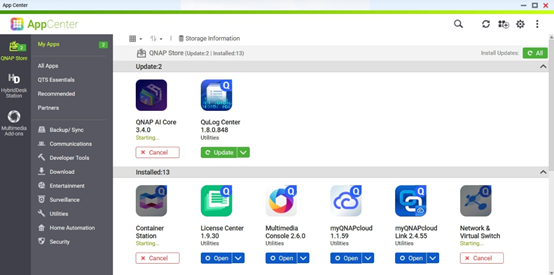
In addition to QTS system firmware updates, QNAP will also notify you when updates are available for your installed applications.
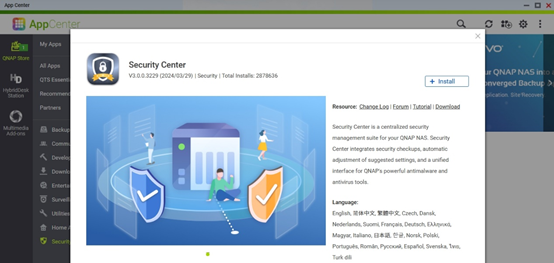
It is recommended that all QNAP users install the Security Center app for a more secure overall user experience and alerts.
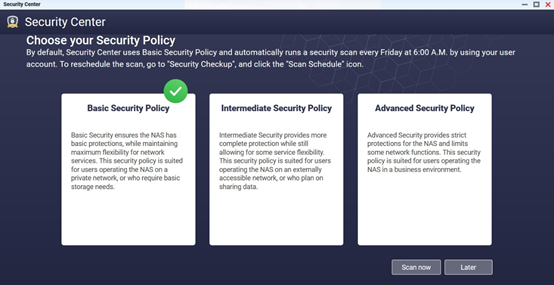
The QNAP Security Center app provides users with basic, intermediate, and advanced security policy recommendations. It scans the entire NAS device and offers recommendations based on the scan results. Following these recommendations can significantly enhance the security level of your NAS device.
Feel secure by consistently updating and maintaining good habits
We can see that major international companies often discover and report vulnerabilities as well as version updates on an ongoing basis. To ensure that fewer users are harmed, some attack methods and critical information aren’t fully disclosed to the public. Detailed content requires access through developer accounts or contracts with customers. QNAP operates similarly to these major international companies to ensure timely release of vulnerability patches. For those needing more detailed information, explanations are scheduled after system updates to protect more family-oriented users.
Fixing security vulnerabilities can be compared to priority-ranking in a hospital emergency room. The most important and severe issues are prioritized and addressed first, followed by less critical ones in descending order of severity.
If the issue is not critical and the solution is known, it’s generally acceptable to first test the update on devices in a test environment before applying it to the production environment. However, if the issue is difficult to resolve yet you want to continue operation without updating the system, it’s necessary to implement appropriate isolation and protection measures and wait for the vendor to release a revised update that addresses the problematic patch. This is a compromise that sometimes occurs in the industry.
For general home and small studio NAS device users, it is commonly recommended to keep your system updated to the latest version. If your device frequently needs to transfer files over the internet to your NAS or you need to access pictures or data on your NAS from your mobile network while working or traveling, make sure to update to the latest version and implement the previously suggested security measures to help mitigate the risks of your important data, sensitive information, family videos, and private photos being leaked. But more importantly, it is important to prevent your NAS from being used as a springboard device to launch attacks on others. Hackers often exploit compromised devices to carry out illegal activities to avoid being detected and identified.
The reason why Hackers often choose various NAS devices as attack platforms is that users frequently make these devices accessible on the internet, and more importantly, because NAS has significantly expanded functionalities in recent years, with support for virtualization, containers and the like, so that hackers can deploy and install ready-made tools onto compromised NAS devices for various types of attacks. Therefore, robust protection and security measures for NAS devices are more critical than ever, and we need users to collaborate with us to maintain the security of these environments.
In order to make your QNAP NASdevice more secure, it is recommended to maintain good habits as follows
Continuous learning: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and QNAP security advisories to enhance security awareness.
Regular inspection: Regularly check the security settings and logs of the device to promptly identify and address any abnormal situations.
Choose apps carefully: Only install apps from reliable sources and update apps regularly.
Secure network: Make sure your network environment is safe and use tools such as firewalls and VPNs to protect your important data.
Through the above measures, we can better protect our QNAP NAS devices and data. In today’s digital age, cybersecurity threats are everywhere. Remaining vigilant and implementing appropriate protective measures is crucial to prevent your devices from being used as tools by hackers. QNAP also strives to maintain the overall information security of the QTS and QuTS hero ecosystems to ensure that users worldwide can update to the most secure versions promptly. Together, we can build a more secure digital environment.